In the ITIL training framework, availability is determined by three key aspects: Reliability, Maintainability, and Serviceability. Reliability is the measure of how long a service can perform without interruption. Maintainability is the measure of how quickly a failed service can be restored. Serviceability is the measure of how effectively third party suppliers deliver their services. These aspects of availability management are discussed in most online ITIL trainings and may be common knowledge to the IT service owner. However, there are intricacies regarding how these factors fit into the ITIL availability management process. Here’s all you need to know about these important aspects and activities of the ITIL availability management process.

Reliability
When it comes to ITIL availability management, reliability is the measure of how long a service, component or configuration item can perform its agreed function without interruption. This is an important factor in service delivery because, in theory, it is expected from a service to work without any interruption or outage. For instance, if a service is performing above the agreed service level targets for more than 1000 minutes, this shows its reliability aspect. And as you can guess, the more reliable a service the more quality will be delivered to the customer.

Maintainability
In the ITIL availability management framework, Maintainability is the measure of how quickly and effective a service, component or configuration item can be restored to normal working after a failure.
Let’s consider a search service that stopped serving properly. If it takes 5 minutes to recover this server back into regular operation, this is a parameter about the maintainability of the service that needs to be managed with ITIL availability management. Note that, failure in the service is not just the outage of the service.
For instance, if the agreed ITIL service level for the search service is to return the results under 100 milliseconds, and if the search service started to return the results in more than one hundred milliseconds, this is a failure as well, although it is not an outage. This should be fixed as well since it does not meet the agreed service levels.

ITIL Availability Management: Serviceability
And the last important aspect is Serviceability. Serviceability is the ability of a third party supplier to meet the terms of their contract often including availability, reliability and/or maintainability. If an IT Service provider is getting an external service from a partner or supplier externally, service levels that have to be met by the supplier are written down in underpinning contract which is signed off between the IT Service provider and business.
For instance, if the IT Service provider requires at least 98% availability during hours of operation for the service, at least 1000 minutes of work without any interruption or outage, or if the IT service provider expects the supplier to fix a problem with the service in less than five minutes, these are all examples about Serviceability. Since it is an important aspect, all these concerns should be carefully negotiated between the IT service provider and supplier before signing off the underpinning contract.
ITIL Availability Management: Process Activities
This figure summarizes the process activities. As you can see in the figure, there are two types of activities fundamentally: reactive activities and proactive activities. Reactive activities include monitoring, measuring, analyzing, reporting, and reviewing service and component availability, investigation of all service and component unavailability and investigation of remedial actions. Reactive actions are taken to monitor whether the agreed availability levels are met and if there are unavailability points for services or components, root causes of the unavailability are found and corrective actions are taken respectively to meet the agreed service levels in availability.
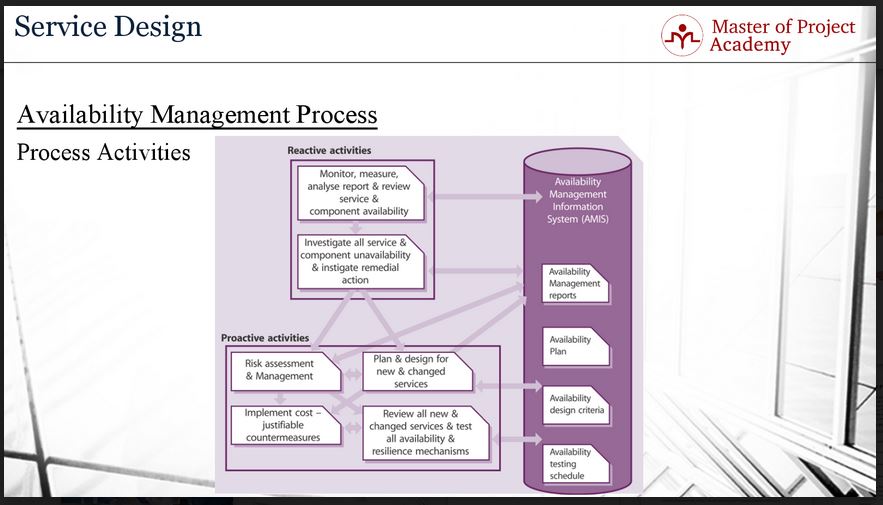
On the other hand, in IIL availability management, proactive activities are taken in order to prevent falling below the agreed level of service and component availability. Proactive activities are:
- Risk assessment and management
- Implementation of cost-justifiable countermeasures
- Plan and design for new and changed service
- Review of all new and changed services
- Test of all availability and resilience mechanisms.
As you see, these reactive and proactive activities feed the ITIL Availability Management Information System which stores the availability related information of an IT Service Provider. This system includes ITIL availability management reports, availability plan, availability design criteria and availability test schedule.
In summary, ITIL availability management measures three important aspects: how long a service can perform without interruption (Reliability), how quickly a service can be restored when it has failed (Maintainability) and how effectively a third party supplier deliver their services (Serviceability).
The ITIL availability management process has a set step of activities in place to avoid system failure and to ensure that the service is available to the customer at the agreed standards. ITIL availability management is a process that is especially important during the Service Design stage of the ITIL service lifecycle and also in the Continual Service Improvement stage of the ITIL service lifecycle.
Without ITIL availability management, services run the risk of failing more often than it should and that could cost revenue if the customers move their business elsewhere because the IT service provider produced unreliable services. This is why it’s important to agree upon standards for Reliability, Maintainability, and Serviceability. When these three aspects are measured against the standard and found to fall short of expectations, the problem can be addressed with contingency plans that were devised after risk assessment in the ITIL availability management process.
