ITIL foundation certification training supports the concept of a configuration model to consolidate the interactions between IT service assets, configuration items and infrastructure. This is a useful tool in ITIL Service Transition stage of the ITIL service lifecycle. Let’s refresh our memories regarding the definitions of service assets, configuration items, and infrastructure. A service asset is a thing or person that is useful or valuable to an IT service. Configuration items are any components that need to be managed in order to deliver an IT service. An IT infrastructure is the composite hardware, software, network resources and services required for the existence, operation and management of an enterprise IT environment. The configuration model connects all these assets and configuration items to smooth over any problems that might arise from interactions between configuration items and assets when changes occur in the IT infrastructure.

As described in online ITIL training, details and information of each configuration item are stored in configuration records. The service asset and configuration management process supplies a model of services and the infrastructure by recording the relationships between the configuration items. The configuration model gives detailed relationships of a service with other services, assets, and infrastructure. Which service is serviced by which infrastructure, which service is hosted by which application, which service is supported by which asset etc. are shown in configuration model.
What Does It Support?
The configuration model of an IT service provider supports among other things the evaluating the impact and cause of incidents and problems. Since the configuration model shows the interaction and relationship of services, infrastructure, and assets with each other, it will ease to find the root cause of an incident and problem. Failure of a service can be related to the application hosting the service, or another service supporting the service etc. The configuration model will show the relationships and help to address the problem. It is a useful tool to identify possible problems that might not have been thought of before the service is launched in a live environment during the ITIL Service Operation stage. This will also help to do risk management.
A change in a service can affect the other services or configuration items that are related or interacting with the service. Evaluation of the impact of the change can be facilitated by a configuration model. Since the configuration model includes and depicts the relationship of configuration items, evaluating the impacts of changes, which applications, which services etc. will be affected due to a change can be seen easily with the help of the configuration model. The business and IT service provider can use this information to decide whether the impact of the change is too risky or whether it will be safe to roll out the change.
Similarly, planning and design of new or changed services and planning the updating of technology and software can be done with the support of configuration model. In this way, consistent, efficient and effective service management can be ensured. When updating a service, or adding a new feature to a service, it needs to be compliant and supported by the other interacting services and configuration items that are in relation with the regarding service. Since the configuration model shows these relationships of configuration items with each other, how a change will affect other parts of the IT service provider can be seen with the help of it. In this way, the configuration model is not only useful in the Service Transition stage but also in the Service Design stage. The configuration model will need to be revised every time that a new service or changed service is implemented.
The configuration model
This figure shows an example configuration model for a “Banking Core Service” with other parts of the IT service provider. As you see, there is a contract between the customer and IT service provider for this service and service level package defines the agreed service level targets in the contract between the customer and IT service provider. Since the banking core service is a running service of the IT service provider, it is part of the service portfolio as well. Therefore, this is shown as a relationship in the configuration model.
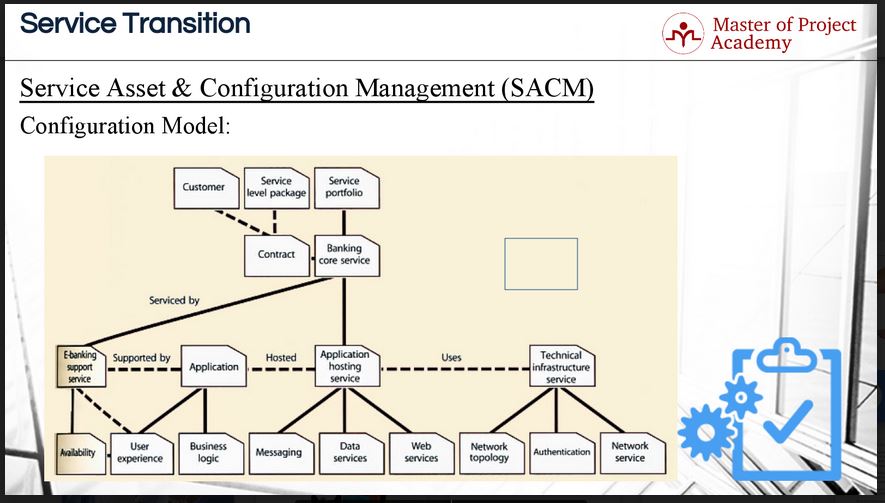
The bottom part of the figure shows the servicing relationships of the banking core service. These are the E-Banking support service and Application Hosting service mainly. The E-Banking support service has relationships with availability and user experience and is supported by the application. The application has relationships with user experience and business logic and provides hosting to the application hosting service. An application hosting service has interactions with messaging, data services and web services and uses technical infrastructure service. The technical infrastructure service has relationships with network technology, authentication, and network service.
In this way, there is an interconnection between availability, user experience, applications, business logic, the application hosting service, messaging, data services, web services, technical infrastructure services, network technology, authentication and network services. All of these services and configuration items can run independently, but they are interconnected and if one fails, there will be a domino effect with failures all across the system. The configuration model allows service owners to inspect what the impact will be if a failure occurs and can mitigate the risks accordingly during the Service Transition stage. This means that there will be no surprises when the service is rolled out to a live environment in the Service Operation stage where the customers will come in contact with the service.
