Capacity planning forms part of the capacity management process within the ITIL foundation framework and it’s included in many ITIL foundation practice exams. Capacity management is a key process in the Service Design stage of the ITIL lifecycle. Without capacity planning, an IT service provider can either spend excess costs for the realistic business requirements or fall short on delivering ITIL service level targets. Good online ITIL courses also explain that there are two balancing acts that forms part of the capacity planning process and that there are several interactions between processes in the capacity management framework.

The two balancing acts in capacity planning
Cost and capacity
In IT capacity planning, there are two dimensions in a balancing act. The first dimension is the balance between costs and capacity. In other words, ensuring that the processing capacities satisfy the business requirements at justifiable costs and will be used as efficiently as possible. Let’s consider that the business requirements asked to support 100 000 users for a service. Based on your calculations, you estimated that four servers and two server administrators can ensure this capacity requirements. And during operation, if only 50 000 users are using this service, then, only half of your capacity will be used. This means that you had to spend extra cost for additional capacity although you could have sufficed the operation of 50 000 users. This is an example of bad capacity planning.
And the opposite case will cause service degradation, which must be taken into account during capacity planning. If 200 000 users will demand this service, after 100 000 users, service degradation will occur. This will affect the service quality. Therefore, there is a balance that must be matched between costs and capacity.
Supply and demand
The second dimension that has to balance during capacity planning is supply and demand. The available range of processing services must be aligned with the current and future requirements of the business. As in costs and capacity, the demand for a service must be supplied by the IT service provider. Good capacity planning means that the IT service provider will be able to deliver on the demand from the customers.
Processes affecting capacity planning
There are three sub-processes of the capacity management process that affects capacity planning. The first sub-process is Business Capacity Management. BCM is the responsible activity that follows the future business requirements for use in the capacity plan. There can be changes in the capacities of provided services by an IT service provider. Some services might be in high demand while some services are not demanded that much. Or a popular service can lose its popularity over time. Consider the instant match score providing service of a mobile operator. During a world cup period, it might be demanded highly and the demand can fall down rapidly after the completion of the world cup tournament. Therefore, due to changing future business requirements, business capacity management aims to meet the required capacity and optimum capacity for the provided services which contributes to capacity planning.
The second sub-process that affects capacity planning is Service Capacity Management. This process aims to gain insight into the performance and capacity of IT Services. The resources used by every IT Service are recorded, documented, and analyzed for use in capacity planning. The actual capacity performance of the services is measured and compared against the agreed capacity requirements. Based on the outputs, if the required capacity cannot be met, corrective actions are planned and the capacity plan is revised accordingly.
The third and the last sub-process that affects capacity planning is Component Capacity Management. CCM is responsible for the aspects of capacity, utilization, and performance of configuration items. Here, data in the capacity plan are gathered, recorded and analyzed. Similar to the Service Capacity Management sub-process, the component capacity management sub-process is responsible for the actual performance of the configuration items and whether they can meet or exceed the agreed levels.
How capacity planning and capacity management interacts with other parts of IT service management?
This figure describes the interaction of capacity management, including capacity planning with other parts of the IT Service Management. As you see, business requirements are generated based on the current service portfolio of the IT service provider. Either updates or changes to existing services are required or development of new services are required by the business. Then, the Business Capacity Management sub-process of the capacity management process evaluates the business requirements and these requirements are turned into service level agreements. Service level requirements and design of the services are initiated. Based on the service design, service capacity planning and component capacity management sub-processes evaluate the actual performance of the service to check whether the planned and desired targets can be reached by the designed services.
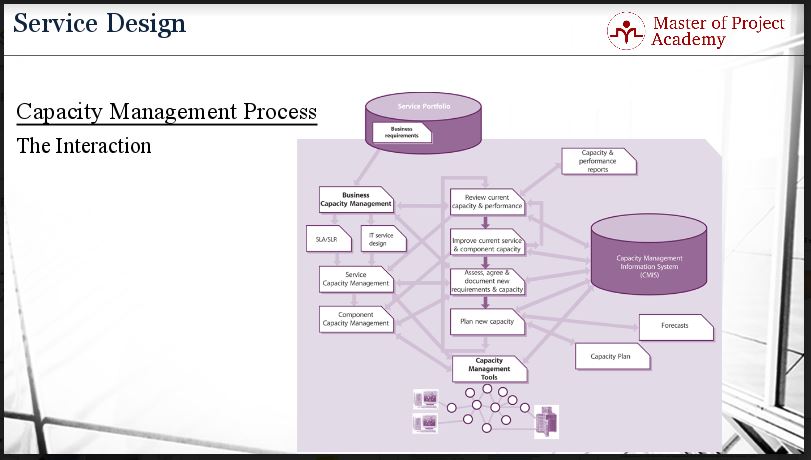
These are the steps which are done in the scope of the capacity management process.:
- Review of the current capacity and performance,
- Improvement of current service and component capacity,
- Assessment, agreement and documenting new requirements and capacity
- New capacity planning
Capacity management tools can be used to ease these activities and all these steps are followed, logged and documented under the Capacity Management Information System in an IT Service provider.
The capacity plan as part of capacity planning
The capacity plan is the important and major output of capacity planning. Based on the service level targets and requirements, IT service provider has to meet the targets agreed with the customer or business. How to reach and ensure sustainable capacity for the provided services are documented, while corrective actions and preventive actions for the capacity requirements are also covered in the capacity plan.
The capacity plan is also used for the capacity of the IT infrastructure. It contains information on three fundamental areas. These are:
- Current use of services and components
- Forecasts on IT capacity
- Costs forecasts for providing IT services in the agreed manner.
If ensuring the required capacity will cost to the company more than the revenue that will be generated from the service, there won’t be a reasonable business for the company.
Capacity planning maintains connections between different predictions of business requirements and options as well. Let’s consider that an IT service provider uses the same server for its three services. Service A, Service B, and Service C.
In order to ensure and forecast capacity during capacity planning, different scenarios for these services are predicted and evaluated to meet the agreed service level targets and requirements related to capacity. For instance, questions such as “Will we be able to serve properly if Service A is used by fifty thousand users, Service B is used by twenty thousand users and Service C is used by seventy thousand users?” can be asked during capacity planning. Another question can be asked: “Will we be able to serve properly if Service A is used by twenty thousand users and Service B and C are used by forty thousand users?” These kinds of different business scenarios are predicted and forecasted during capacity planning.
Review by: Misty Johnson
