Are you planning to start a project management journey? If yes, then the article is the right fit for you. As in this article, we aim to provide you an intro to Project Management in 5 major steps. Project Management is a worldwide recognized position that comes with a lot of Project Manager roles and responsibilities towards project completion within the associated constraints.
Project managers always thrive to enhance their professional careers and develop management skills through learning. This journey of learning starts with PMP training.
Attend our 100% Online & Self-Paced One-Hour Free PMP Training.
This training lays the foundation for understanding project management practices. It essentially means that the very start of the journey is to acquire knowledge of project management practices.
Now let’s have a closer look at the major 5 steps of the introduction to project management and learn the basics!

Intro to Project Management in 5 Major Steps
It is essential for project management aspirants to learn how to approach complex problems with an easy but highly effective way of solution. These steps include:
- Initiation
- Planning
- Execution
- Monitoring and Control
- Closure
The beauty of these steps is that the overall approach of project management is so simplified. And this simple approach helps the project managers to solve complex problems. Wow! Isn’t it a relief that one does not have to remember a long list to learn the project management approach? But of course, all these steps include many more details, so keep reading!
The PMI standard defines this approach in the form of process areas. These process areas give one perspective to group the relevant processes within each of these process areas. So you have to learn to categorize the overall processes within these process areas and at the time of a specific process area, you need to mainly focus on its processes.
Each of these steps has its associated processes and purpose. In the below sections we will discuss the objective of each of these steps. But first, we need to have a bird’s eye view of the project and project life cycle.
What is Project?
A project is a temporary endeavor undertaken to create a unique product, service, or result. The important point to note here is the term “temporary endeavor” which means that the project is of a temporary nature. Therefore every project should have some start date and end date associated with it.
When we traverse the definition a bit more, we see the term unique product or service. This means that the temporary nature of a project has a unique purpose i.e. to deliver a product or a service that is not a routine delivery. So the scope of the product or service derives from the scope of work. Furthermore, for this specific purpose, the resources will be engaged for a specific time. This means the cost factor will also play a vital role.
Hence a project manager has to deal with various constraints that are associated with the project. Likewise, the project deliverable must fulfill the stakeholder requirements which is termed as the quality of the deliverable.
The main of these project constraints include Scope, Time, Cost, Quality, and Stakeholders. Now the question arises: how these factors are calculated first so that the project managers ensure compliance with these factors? Here comes the role of the aforementioned steps we have highlighted as the project approach.
Creating a new course for professional development, constructing a new airport, and developing an ad to promote a specific product or a service are a few examples of projects.
What is the Project Life Cycle?
The life cycle is the collection of stages that sets the road map for the project – from initiation to closure. The life cycle could be the stages that we have discussed above. That is Initiating, Planning, Executing, Monitoring and Controlling, and Closing.
However, it is not essential that the project life cycle can only comprise of these exact notations and terms. Sometimes the project stages are defined with respect to the domain as well. However, all these stages focus from conceptualization to ending the project.
For example, in a software development project, the project life cycle could be defined as:
- Analysis
- Design
- Development
- Test
- Deploy
Whatever the number or name of the phases, each phase is supposed to have associated objectives and deliverables. And within each phase, the processes related to Initiating, Planning, Executing, Monitoring and Controlling, and Closing must be applicable. This is depicted in the following figure – The Project Manager’s sphere of influence by PMI.
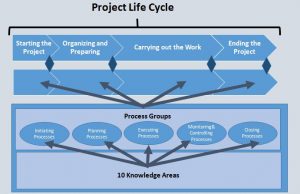
Since we have touched base on the project and project life cycle basics, now we can proceed with the introduction to project management in 5 major steps. In the following sections, we will go step by step and cover the basics of each stage one by one.
After helping over 125,000 professionals in more than 180 countries with a 99.6% first attempt pass rate, we have prepared a seven-step PMP study plan. Read this PMP study plan and create your own best PMP study plan accordingly.
Intro to Project Management: Step 1 – Initiation
Project Initiation is one of the most important stages of the project. At this stage, the projects are conceptualized from the wish and need. This is one of the vaguest stages of the project. At this stage, the opportunity and justification of this opportunity are identified.
Business Case
Teams are assembled to define business cases. Sometimes the business case is handled externally to the project boundaries and it is assumed that the business case has already been prepared, assessed, and approved externally to the project. However, this does not mean that the project manager is not supposed to work on the business case.
The key point addressed in the business case is to examine whether your project is feasible in terms of the project constraints and above all whether the project will add value to the organization. A lot of effort is put into the business case like whether the investment made will bring profits and what will be the time of the return of investment. After a detailed feasibility study business case is prepared. Then the top management decides the way forward whether to proceed with the project or not.
Project Charter
Once the project is approved, the next main area to address is chartering the project. The project charter is the key deliverable of this stage. At the very start of the project, it is important for any organization to officially authorize the project and assign the project manager. This entitles the project manager with the authority and responsibility towards the project. Also, the main stakeholders become aware of the point of contact as project managers have to closely collaborate with the stakeholders throughout the project.
Watch our “What is Project Charter – Benefits of the Project Charter” video
At this stage, the project manager also identifies the stakeholders that have an interest and impact on the project to perform stakeholder management subsequently.

Intro to Project Management: Step 2 – Planning
The project charter gives a high-level overview of the project. This is the starting point for the project manager as she or he is authorized for the project. Now the project manager needs to start with the project planning. This is the stage of detailing how the project will be carried out.
Master Plan
Planning sets the road map for the subsequent stages of the project. The key deliverable of this stage is the master plan document. This document is prepared to address all the areas of project management. These areas are known as knowledge areas. These project management knowledge areas include Integration management, Scope management, Schedule management, Cost management, Quality management, Risk Management, Human Resource Management, Communications Management, Procurement Management, and Stakeholder Management.
Watch our “What are the PMP®, PMBOK®, Project Management Knowledge Areas?” video
You may have subsidiary plans for each of these knowledge areas. These subsidiary plans will be part of the mast project plan.
Address the Changes
Since the project planning is the transformation stage of the project where the unclear aspects are chalked out to bring clarity to the project activities within all the knowledge areas. This also means significant changes may occur throughout the project life cycle. These changes may trigger a need to revisit one or more of the planning processes and possibly some of the initiating processes. This progresses detailing of the project management plan is called progressive elaboration, indicating that planning and documentation are iterative and ongoing in nature
Intro to Project Management: Step 3 – Executing
Once you are done with planning, it is time to execute what you have planned. As we mentioned earlier the master plan should cover all the areas related to project management. The level of detail of the plan will help you prepare for the scenarios that may arise at a later stage. Therefore we can say that while executing stage, you perform the project activities in accordance with the project management plan.
Address the scope of work
You are required to address the scope as defined in the project scope statements. In addition to this, you may need to cater to the changes but you implement the approved changes as you have identified the scope of work. This scope of work derives the required effort and cost which are determined during the planning. Depending on the effort requirement and resource plan, you induct the resources to carry out their relevant jobs. Once you induct the resources, they will collaborate with each other in line with the communication plan. Furthermore, you also initiate the procurement based on:
- the procurement management plan
- carried out bid/vendor evaluations.
Address the Risks
During the project execution, you also ensure that the risks are identified and addressed. Focus on managing the project stakeholders is another important point. You will also need to conduct the meetings within teams and with the stakeholders. Furthermore, you will disseminate the project information to project stakeholders.
Follow the Plan or Change the Plan
So in the execution stage, you are responsible for the execution of what was planned in each knowledge area. The most important thing here is while executing you got to manage the resources as the team resources are at the maximum level of importance at this stage of the project. Your leadership skills like influencing people, problem-solving, and negotiations will be highly utilized at this stage. Moreover, conflict management is another area that may need more attention during execution.
Knowledge Management
There is another important aspect of the project to mention here, during the project execution stage, you also focus on knowledge management. All the artifacts that are produced during the project will become part of knowledge. These artifacts may include:
- Deliverable
- Documentation
- Risk and Assumption
- Estimations
- Changes
- Work items.
Furthermore, you also manage the Quality Assurance activities in line with the quality plan during project execution.
Intro to Project Management: Step 4 – Monitoring and Controlling
As the project progresses with time the project team works on the execution of the plans. Even if the project manager manages the project, but there is still a possibility of slippages. These project slippages can be with overruns and project overruns in terms of schedule and cost. Likewise, there is a likelihood that the actual scenarios are more promising than the planned ones. Moreover, unanticipated situations may also occur which may impact the project attributes.
Monitor and Control the deviations
Hence in the Monitoring and Closing stage of the project, you need to focus on all the possible factors that may impede your project. In other words, we can say that in the Monitoring and Controlling stage, the project manager’s focus is to track, review, and orchestrate the progress and performance of the project. The project manager also identifies any possible changes to the plan and initiates the corresponding changes.
Change Management
In addition to this, the project manager’s challenge is to control changes and recommend corrective or preventive action in anticipation of possible problems. The project manager monitors the ongoing project activities against the project management plan. They compare the project information with the baseline project performance measurement. In addition to this, a good project manager puts their efforts to influence the factors that can cause change. Once the change is desired, it passes through a defined change control process. This process ensures that only approved changes incorporate within the project. As each change affects the project time, cost, and scope.
Compare with the baseline
The project manager will use the tools like Expert Judgement and Data Analysis to take appropriate measures. As this helps the project manager to identify the quantity or impact of deviation from the baselines. This requires a variety of Data analysis tools and project management techniques like:
- Alternative Analysis,
- Cost-benefit Analysis,
- Earned Value Analysis,
- Root Cause Analysis,
- Trend Analysis,
- Variance Analysis.

Intro to Project Management: Step 5 – Closing
On the completion of the project, it has to be closed formally. This requires that the project manager carries out all the activities in order to conclude all activities across all project management process groups to formally complete the project, phase, or contractual obligations.
This stage verifies the completion of all the defined processes to close the project or a project phase, as appropriate. It also formally establishes the project or project phase closure. At this stage, you ensure the closure of all procurement activities. In addition to this, you will perform team members’ assessments and release project resources.
At this stage, you address all project areas so you can officially declare the closure of the project. Hence one can say that at the time of closure of the project:
- There is no pending scope of work
- All the agreements are complete and close
- The client approves all the committed artifacts that you delivered during the project
- The quality measures meet the criteria as per the quality plan
- Assess and release the project’s human resources
- The knowledge repository has the latest artifacts – project reports, lessons learned documents
- Ensure the incorporation of all approved changes within the project
PMI and Process Groups
Our main focus on these steps is in line with the professional standard by PMI. According to PMI Project Management Professional Body of Knowledge (PMBOK), these stages are termed as Process groups. There is a total of 49 processes. The process groups segregate these processes. Each of the processes plays its own important role in project management practices.
Tips for Successful Project Management
We have discussed the high-level overview of key focus areas in the different stages. Here we give a couple of tips for effective and successful project management.
Requirement – Focus on Customer Need
The gathering and analysis of requirements are one of the cornerstones. Everything in the project is based upon the requirements analysis as this targets the strategic purpose of the project. The more accurate you assess the requirements, the more the chances to succeed.
Plan – Close to the Reality
The project plan must be as close to reality. In order words, you can say that your brainstorming, experience, connection with the right sources, and expert judgment play a vital role to understand the nature of the project.
Set the environment for success
Your team is your asset. Take care of your project team. You need to develop them and motivate them as you have to face the challenges together. Develop a culture of trust, respect, healthy criticism, and win-win situations.
Lead from front
Project managers have to be proactive, they have to deal with the customers and other project stakeholders. Project managers also deal with vendors. It means they have to collaborate with several groups at the same time. Project managers have to keep all the sub-groups and parties synchronized, and well aware of the latest updates. You will need your leadership skills to pro-actively handle the situations. These skills include negotiation, influencing, confrontation,
Define measures – Monitor on a frequent basis
Throughout the project, you need to monitor the project’s progress. This will help you identify your position with respect to the desired criteria. So that you can take appropriate measures to bring the variations within control measures. You must collect project information for this sake.
Disseminate Information – Communicate effectively
Manage the expectations of your stakeholders and communicate with your stakeholders on a frequent basis. You need to disseminate information to the involved parties in the desired formats and measures. This helps every one to get the latest updates and happenings within the project.
Manage Risk
The dynamic nature of the project and its environment, require project managers to keep on identifying and managing the risks on a frequent basis. First, you need to properly address the identified risks. Secondly, you need to ensure the identification of possible upcoming risks. This will help you address the new risks well ahead of time rather than handling the disasters at a later stage.
Intro to Project Management in 5 Major Steps – Conclusion
In this article, we provided you an intro to project management in 5 major steps. These 5 major steps are Initiating, Planning, Executing, Monitoring and Controlling, and Closing. Within each of these steps, we highlighted the focus areas. We can say that these are the main functions that project managers perform to manage the project.
We are aware of the fact that the aspirants keep on looking for information that helps them to initiate their learning. Hence we aim to boost your learning of the practical aspects. In this regard, we also shared a couple of tips for effective project management. Hope you find this article helpful.
5 / 5 stars

