In 6 Sigma, CTQ is an acronym that stands for Critical-To-Quality. Customer requirements, which are identified as CTQs, are actually a handful of elements that are considered critical to the executive team in determining the success of the project/product/process. CTQ trees were originally developed as a part of the Six Sigma approach. However; you can use them in a variety of situations, including when you are developing products, processes, and services for your internal customers.
Attend our 100% Online & Self-Paced Free Six Sigma Training.
For example, an instruction such as ‘Improve customer service’ is too broad to do much with it. However, by using a CTQ Tree, you can drill down this general goal, and identify specific and measurable requirements that you can use to improve performance. Determining Critical-to-Quality customer requirements is a part of Lean Six Sigma training, which can be done through a Lean Six Sigma course. Let’s look at how we identify and deal with QTC parameters.
What is Critical to Quality Tree?
CTQs are the internal critical quality parameters that relate to the wants and needs of the customer. The (internal and external) customer requirements get translated into Critical-To-Quality (CTQ) features. These CTQs define the criteria to evaluate what good looks like i.e., how well the project scope and deliverables meet customer requirements. CTQ is a simple, yet powerful tool that translates customer needs into Meaningful, Measurable, and Actionable metrics for people or groups of people.
CTQs answer this question: How does my work relate to the customer requirements, and how do I know when I have fulfilled them? CTQ helps you to understand the customer’s general requirements in more specific terms. CTQs serve as a bridge between the internal process, its deliverables, and customer satisfaction.
How to identify CTQ parameters?
This figure shows the CTQ identification process using a simple example.

It is a step-by-step process to identify CTQs for critical customer requirements. Notice the order of the events that help to identify QTCs. Here the process is broken down into seven steps:
- VoC Six Sigma: It has been noted in the words of the customer
- CTQ Name: It has been noted in the words of the organization
- CTQ Measure: As identified by the organization
- CTQ Specification: As specified by the organization
- Defect: As defined by the organization
- Unit: It is an organizational / process metric
- Opportunity: As determined by the company/process
How to develop a CTQ Tree?
Identify critical customer needs
We first need to identify the critical needs that the product or service has to meet. Please make sure to do a CTQ Tree for every need that you identify. During this first step, we’re essentially asking: ‘What is critical for the characteristics of a product or service?‘ It’s best to define these needs in broad terms. If it is not possible to directly ask customers about their needs, then the project team can brainstorm their needs with people who deal with customers directly – Salespeople and Customer Service Representatives – as well as with your team.
Identify quality drivers
It is important to identify the specific quality drivers that have to be in place to meet the needs that we identified in the previous step. Please remember, these are the factors that must be present for customers to think that you are delivering high-quality products. Note that it is very much necessary that we identify all of the drivers that are important to the customers. Tools such as KANO Analysis will be useful here. KANO model will help you identify product features that satisfy the customers.
Identify performance requirements
Finally, we need to identify the minimum performance requirements that we must satisfy for each quality driver, in order to actually provide a quality product. Here it’s important to remember that there are many things that will affect an organization’s ability to deliver these.
Once we’ve completed a CTQ Tree for each critical need, we’ll have a list of measurable requirements that we must meet to deliver high-quality products.
CTQ Tree Examples
Have a look at a CTQ example. On the basis of this case study, we’ll prepare a CTQ tree for one of the critical customer requirements.
Before you begin preparing a CTQ tree you have to:
- Identify your customers
- Collect Voice of Customer data
- Analyze VoC data
- Prepare a list of CTQs
- Choose one CTQ and prepare a CTQ tree only for that CTQ.
Please note that you will need to prepare a separate CTQ tree for each CTQ. Do not try to combine multiple CTQs under one CTQ Tree. Let’s look at the background of this simple case study regarding pizza delivery, the pizza company must have surveyed 10000+ customers. Post collecting VoC data, they must have analyzed it systematically. Post analysis, they came up with critical customer requirements; which were voiced by the majority of their customers.
This figure shows what your CTQ tree would look like for one of the critical needs identified i.e. “I need my pizza now”
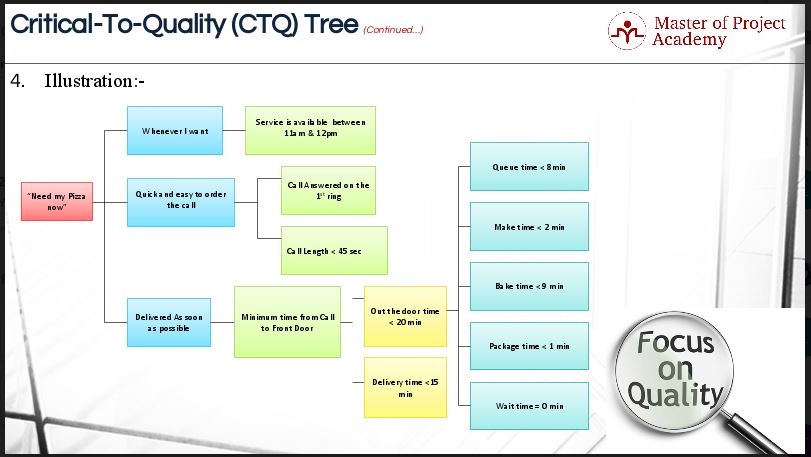
It’s horizontally-placed critical to the quality tree. You can also prepare a CTQ tree that is vertically placed. This is just a representative CTQ tree and is not complete in every respect. The purpose here is to make you understand the topic.
How to read the CTQ tree?
How do we read or comprehend the tree? “I need my pizza now” has three quality drivers. The first one is “Whenever I want”. The customer says I need my pizza whenever I want. It means I want it anytime during the day. That is the VoC. Over here, VoB (Voice of business) says that the service is available between 11 AM and 12 PM. It means that if the customer needs pizza at 8 AM, he/she will not get it at all.
The second quality driver is ‘Quick and Easy to Order.’ In order to ensure that the pizzas are quick and easy to order, the first metric or performance requirement that the business has to meet is ‘Call answered on the 1st ring’. The standard expectation is that every call that all calls that the pizza store receives should be answered on the 1st ring. The business problem may be related to this performance requirement. The Six Sigma project needs to validate the non-performance towards answering the call on the 1st ring. The team may need to look into the historical calls data, for the past six months, to check how many calls were actually made at each counter in the pizza store, how many calls actually rang but; were not picked up, and how many calls were abandoned because they were not picked up in the first ring, etc. The data has to speak the performance story.
The question for the business is: How to get it done? Critical questions, at this stage, could be:
- Do we need to increase the number of people on board?
- Do we need to increase the number of telephone lines?
- Do we need to appoint one person just to pick up the call?
Providing answers to these questions might end up in having a new CTQ. That is how you need to read and prepare the CTQ tree.



One thought on “Six Sigma Critical to Quality: 7 Steps to Produce CTQ Tree”
Comments are closed.