In the ITIL change management process, which forms part of the ITIL Service Transition stage of the ITIL lifecycle, there are several models and workflows that form part of the process. These change management process models and workflows ensure that any changes are done in a controlled manner. Online ITIL courses discuss all the workflows that exist in the change management process. In this article, we will discuss the workflow for normal changes, i.e. changes that are neither emergencies nor low priority changes as covered in ITIL foundation training.

Pre-defined change management process
Changes should be done in a controlled manner. Predefined change management process models are helpful in managing change in an IT Service Provider. IT change management process models define expected outputs for predetermined inputs. For instance, an emergency change would have a change management process workflow and a request for change (RFC) would have a different workflow. These are determined and structured under change management process models and change workflows.
Change management process support tools
Support tools can be used to manage the required processes. For instance, in order to follow the lifecycle of an RFC, an issue tracking system or software can be used. The last status of the RFC, such as waiting for approval or rejection for a specific reason can be tracked and recorded in these kinds of software applications or systems.
Steps in change management process model
The change management process model includes steps that should be taken to handle the change including handling issues and unexpected results:
- A list of steps that should be taken
- Chronological order of the steps
- Roles and responsibilities
- Timescales and thresholds
- Escalation procedure
By having a list of steps that should be taken, the IT service provider will be prepared for any situation and will know what to do to initiate and follow a change request. Or in the case of any unexpected issue such as a failure during the implementing the change, the process for handling these extraordinary situations called ITIL Remediation plan is written down in change management process models.

The chronological order of the steps that should be taken with any dependencies or co-processing should be defined. For instance, a prerequisite for initiating an RFC can be the documentation of the scope and reasons for the change in the RFC template document first. Or, implementing a change can be possible only if the service owner of the regarding service has given the final approval for the change. Roles and responsibilities are included and clearly defined in the change management process model as well.
Timescales and thresholds for completion of the actions are also included in the change process models. For instance, an approval for an RFC cannot wait for more than one business days in a station. Or, an emergency change request must be implemented in less than three days. These kinds of timescales and thresholds are defined in the scope of the change management process models.
And finally, the escalation procedures are part of change management process model as well. For instance, if there is an emergency change that must be implemented immediately, this must be escalated to the senior management of the company. These kinds of escalations are included in the change management process model. The escalation procedure must not only define to whom the matter must be escalated to but also through what means – a simple phone call, email, status meeting etc.
Change Management Process –Workflow of the Normal Change.
This figure shows the change management process workflow for a normal change.
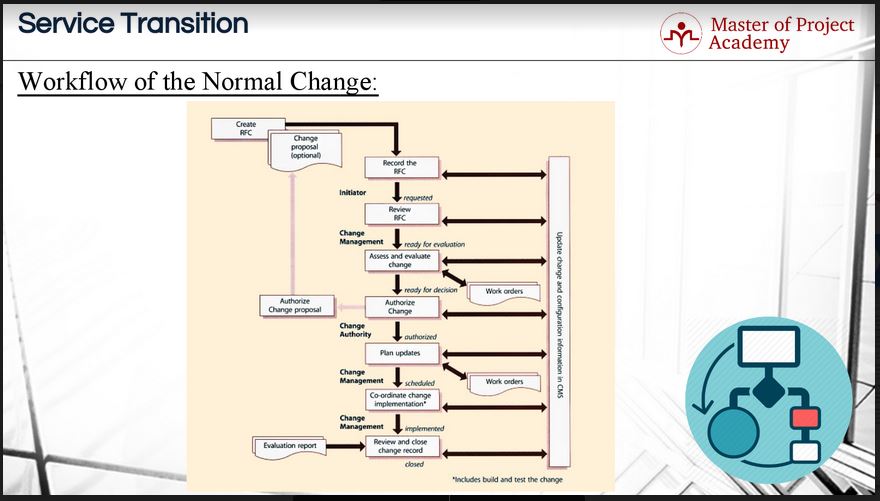
1. Creation of the request for change
As you see, the first step is the creation of the RFC. After the RFC is created, this is recorded in the configuration management system (CMS). Then the initiated RFC is reviewed. The scope, details, and impact of the requested change must be analyzed carefully. After the review of the RFC, the change request is assessed and evaluated in terms of the impacts of the change, the expected outcome, what will happen in the case of failure etc. Necessary work orders are created if required.
2. Authorization or rejection of the change request
After the change request has been assessed and evaluated under the change management process, a decision is taken in the next step. Either the change request is authorized and change proposal is sent to the initiator for review or change management authority rejects the change.
3. Planning of steps in change process
If the change request is authorized, then changes are planned in the next step. The service owner will ascertain when the change will be ready and in which release, as well as when it will be implemented. These are planned during the plan updates step. At the end of this step, changes are scheduled for implementation.
4. Coordination and implementation
Then, in next step, this change is coordinated and implemented with other several change requests that might have been initiated. After successful implementation of the change request, a change request record is reviewed and closed in the last step. And an evaluation report is created as an output of this step. Note that, this figure describes the high-level steps of the workflow of a normal change for the IT Service Provider. Steps depicted here can have several sub-steps. And in each step, the results and history of the change request are updated and recorded in the Configuration Management System.
It is important that the relevant parties in an IT Service Provider follow the change management process steps closely so that any mishaps can be avoided once the service goes live. One of the crucial steps in the change management process is the request for change or the RFC. Without proper documentation as is compiled in the RFC, it is difficult to trace back failures in the system.
Review by: Jacob Sims

3 thoughts on “ITIL Change Management Process: Models You Need to Know”
Comments are closed.