After reading this article, you will have a firm grasp on the definition, purpose, and value of a configuration baseline. Configuration baseline is discussed in-depth in ITIL Courses. It’s an important part of the change management process which in turn is an important process of the ITIL Service Transition stage of the ITIL service lifecycle. ITIL foundation training focuses intensively on the ITIL lifecycle.

Before defining and describing a configuration baseline, we’ll start by defining the baseline. A baseline is the recorded state of an element at a certain time as a reference value. For instance, you plan a project, define its start and end dates and interim delivery points, and dates. This is the planning phase and a project baseline is taken after the planning process finishes. Later on, during project execution, several unexpected risks can occur which can cause delays and extension of the project delivery dates. These actual dates and results are always monitored against the baseline to check whether the project is behind the schedule or ahead of schedule etc. So the main benefit of a baseline to set a point in time against which results can be checked or to which an IT service provider can turn back to in case of a problem in future.
What’s the Definition?
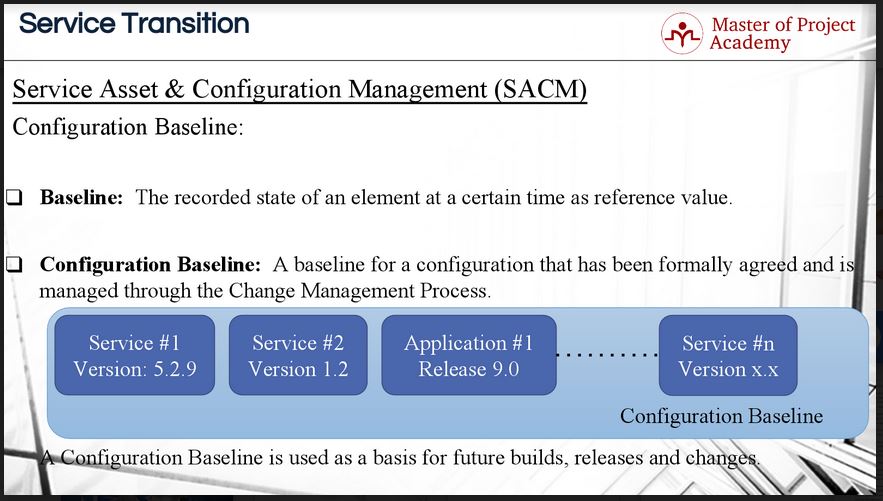
A configuration baseline is a type of a baseline specific to configuration management. A configuration baseline is a baseline for a configuration that has been formally agreed and is managed through the change management process. An IT Service provider will have several services. In order to provide a successful and quality service delivery to the customers, all assets and services must be working properly and in compliance with each other.
Let’s consider that Service 1 has a version of 5.2.9. Service 2 has a version of version 1.2 and Application 1 is at release 9.0. An IT service provider may have several services, assets and configurations and each of these will have a release or version. And the configuration baseline refers to the working state of several configuration items.
The value of a configuration baseline
Since the configuration baseline refers to a working state of several configuration items’ releases and versions, it can be used as a basis for future builds, releases, and changes. Let’s assume that the IT Service provider upgraded a number of services at the same time. After the upgrade, some problems occurred in service management. If the IT service provider has a configuration baseline from before the problems started, each configuration item can be restored to its initial state to recover the problem.
Configuration baseline and performance baseline
A configuration baseline is closely related to a performance baseline. Performance baselines consist of a set of metrics or KPI’s that need to be adhered to in order for a service to run smoothly. A set of performance baselines is agreed upon before the service is deployed. The performance of the service will be checked against the performance baseline on a regular basis to determine whether the service is still running up to standard i.e. does it still add value to the company according to the agreed upon standards. If changes to the services have been made, updated and deployed, the performance metrics must be monitored to see if the changes had an effect on the performance metrics. If the service is still doing well, everything is good. If the performance metrics goes south, then it must be considered to return to the previous version or to update the new version again to fix the bugs. If the updates to the new service affect the performance of other services it’s best to return to the configuration baseline.

What Are the Metrics?
One of the metrics that are considered is component metrics. Component metrics focus on the performance of individual pieces of the IT infrastructure. Utilization Metrics help evaluate usage and determine if services are operating at optimal capacity levels. If services are operating at its optimal level after a release of a new configuration of the service, one can consider that all things are going well and that the new configuration can be built into the updated configuration baseline.
Revisiting service asset and configuration management
Let’s revisit the goals of service asset and configuration management. The goals of service asset and configuration management are to support the control objectives and requirements of the business and the customer. A second goal is to support an efficient and effective ITIL service management process. A third goal is to minimize the number of quality and compliance issues. The final goal is to optimize service assets, IT configurations, capabilities, and resources.
Configuration baseline management is part of all these objectives. If changes to the configuration result in disrupted services, the configuration no longer supports the objectives and requirements of the business and customer. Similarly, if changes to the configuration are no longer effective or efficient due to a version upgrade, it does not support the second goal of service asset and configuration management. Configuration version control against a configuration baseline ensures that the number of quality and compliance issues are minimized which supports the third goal of service asset and configuration management. Finally, using configuration baseline as a part of the fourth goal of service asset and configuration management by optimizing IT configurations.
Therefore, the use of configuration baseline is a critical step in the ITIL service transition stage where service asset and configuration management plays a large role. Without a configuration baseline, there is no safety net to protect the IT service provider against negative effects of changes in versions of IT configurations. Using a configuration baseline allows IT service providers to return to the best state at which their services worked at an optimal level if a new upgrade did not perform according to plan. However, if all the ITIL steps and processes were followed, upgrades to services should not have a detrimental effect on the IT configuration set.
