Companies initiate projects for several reasons. In a medium to large size organization, several departments might be working on different projects. The Project Management Office, also known as PMO, manages the initiation, execution, and successful project delivery in an organization. However, regardless of the influence of the PMO, project cost overruns are inevitable events that happen in every organization.
In order to make the concept of cost overruns more clear, we will be discussing the following in this post:
- Three real-life project cost overruns
- The common reasons leading to project cost overruns
- How to prevent and manage project cost overruns.
- The role of the Project Management Officer in project success
Let’s go through each of them one by one.
Research About Project Cost Overruns
Before going through the details of the project overruns, let’s look at some research about the project cost overruns.
1,471 projects were analyzed, comparing their budgets and projected performance benefits with the real costs and outcomes. Based on this Harvard Business Review (HBR) research, the average overrun was 27%, but that figure hides a far more alarming figure. The graph representing the project budget overruns shows a “fat tail”- a large number of gigantic overruns. One in six of the projects that HBR studied was a black swan, with a cost overrun of 200 percent, on average, and a schedule overrun of nearly 70 percent.
When we surveyed 425 participants who attended our corporate training programs, they reported that schedule delays, inexperienced/unskilled resources, and project cost overruns are the most common issues in their organizations.
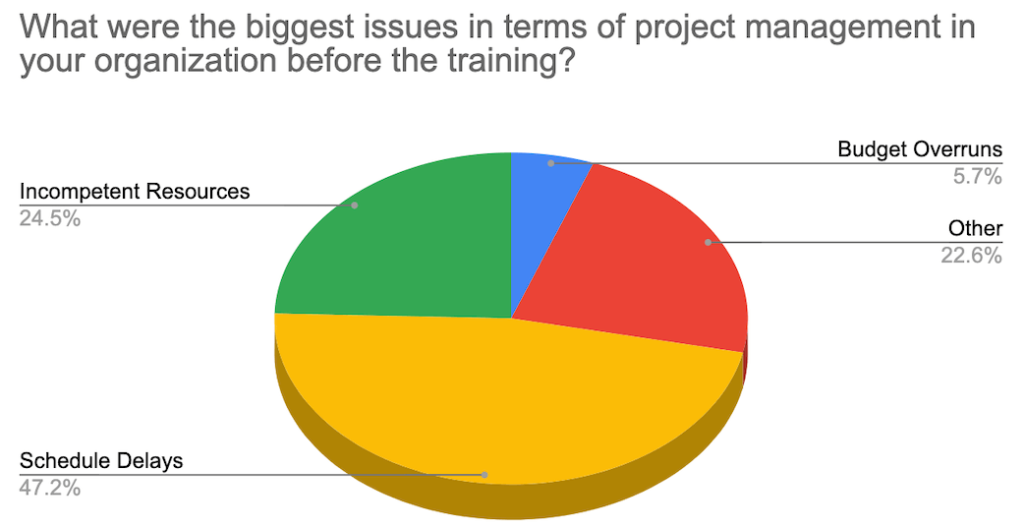
So, if project cost overruns are a common issue in managing projects, what are the reasons, how can we prevent it, and how can we manage cost overruns if we could not prevent it? Let’s go over them in detail.
Real-life Project Cost Overrun Cases
Here, we will provide three real-life budget (cost) overruns caused by different reasons.
- Case#1: The sales manager sells a technically undeliverable solution. Result: the project team works on new features, and this causes a 17% budget overrun.
- Case #2: The HR personnel does not approve the vendor team’s premises access papers on time. Result: The vendor accesses the premises two days later and this delay costs the organization $13,000.
- Case #3: The finance department approves the project budget two days after the deadline. Result: the project resources assigned to the team wait idly for two days and this delay costs the organization $37,000.
Note that these are real-life project overrun cases from our clients. We have trained 200,000+ professionals and I am sure you have experienced similar cases where “non-project” people or stakeholders who are not directly involved in the project caused project overruns. That is why we have launched PM Core™ – Project Management for Business People Training program to create project management awareness among non-project people.
The PMI’s research about PM competency backs up our findings. Based on PMI’s research, increasing of the project management competency and understanding of the business people in an organization can increase on-time project completion by 49% and on-budget delivery by 40%.
Reasons for Project Cost Overruns
There could be several reasons for project cost overruns in an organization. However, the most common reasons are unclear scope definition, irrelevant estimation, unanticipated risks, and unskilled or inexperienced resources. We will be talking about these reasons in detail below.
1- Unclear Project Scope
Having a scope that is not clear, which is ambiguous, or confusing is bound to cause issues. The project team will deliver what they have understood from the project scope. Often, the resources tend to make assumptions and these in the end could prove to be wrong. Whether the scope is not defined or communicated well, or it is not understood correctly, there will be undesirable outcomes coming out of the project. These, in turn, may result in the need for corrections or rework, causing project cost overruns.
2- Inappropriate Activity Estimation
Correct estimations are crucial in the project. Estimation about the activity duration, and the number of resources required, for example, are just a few things that often are incorrectly estimated. Let’s say, we have an activity that could have been done by two resources, but three resources were assigned to complete it. So, you will be incurring costs for an extra, unnecessary resource. Or, if you plan 8 days for an activity that realistically could be done in 5 days. This too will cost you more.
3- Unanticipated Risks
The absence of ineffective risk management is a very common reason for project issues and project cost overruns. Risks related to employees, cost, materials, equipment, suppliers, etc. – all could lead to project issues.
Often, organizations have risk management processes in place. However, the staff assigned to the risk management activities might be inexperienced or unskilled. This could become the reason for overlooked risks, improperly planned or ineffectively managed risks. And, when these risks occur, a higher cost is incurred in managing them. If there is no plan or budget to overcome a risk that has not been anticipated during project planning, obviously, it will impact the schedule and budget of the project.
4- Inexperienced or Unskilled Resources
Assigning a poorly skilled resource to an activity may be a cheaper option. However, when the same resource makes mistakes or takes longer to complete an activity, there will be challenges.
Let’s say, for instance, there is an activity estimated to be completed in five days for a $20,000 cost. This same activity may cost you $5,000 more with an unskilled resource. Resource management in projects is an art. You should neither assign overqualified resources nor underqualified resources. Overqualified resources will increase the cost, but underqualified resources will increase the cost as well.
How to Prevent Project Cost Overruns
Not every cost overrun might seem significant. However, if every project is overspending by 2% or more, for instance, it will add up to a lot at the end of the year. It also means that at the end of the year, there may be no bonuses or incentives. These are the things that the employees are expecting and anticipating.
Unfortunately, it has become a norm for many projects to go over the budget. However, the reality should be different. Fortunately, with good and thorough planning, effective tracking, and supportive stakeholders, you can prevent project cost overruns. Below, we list the top four ways how to prevent project cost overruns.
1- Prevent Scope Creep
Scope creep is basically adding additional functions or features to the new product, work, or requirements that are beyond the agreed-upon scope. Scope creep can happen in any project. And it can cause project cost overruns as well as time delays and decreased satisfaction. Adding an additional feature that yields good results isn’t bad. However, if it is not approved, it is scope creep, and this must be prevented.
There could be many reasons why Scope Creep could occur, such as:
- Lack of clarity on what exactly is required.
- Customers trying to get extra work done for free.
- Beginning with the development of a product/feature before thorough planning is completed.
- Very little customer interaction with the project team.
- Lack of change control.
- Differing stakeholder opinions.
- A poor time or cost estimation.
Fighting Scope Creep is simple. You have to firmly establish the requirements that match the customer’s needs, requests, and expectations. When this is done, it’s important for the project team to have a thorough understanding of what really is required. This step is crucial because based on this understanding, the team will develop and deliver the required product.
So, the project manager must clarify each requirement with the customer. The project team should also clarify the project scope or activities where they have a doubt. The project team should stick to the requirements. And, if there is a doubt, they must get clarification from the project manager. Moreover, no favoritism, nepotism, or bias should be allowed in the projects. Any additions that will be made must be approved first and then incorporated into the product.
2- Acquire the Right Skills Needed
Once you know the project requirements and the customer needs, you should acquire the resources with the right skills. E.g, if an activity requires a senior resource, but you assigned a junior resource, you might think you’re saving money. In reality, the activity may take longer to complete and might exceed your planned cost.
- Learn more about Master of Project Academy’s Leadership Program where your leaders will get instructive and hands-on training through interactive exercises, case studies, templates, and techniques that can be customized to your organization’s specific needs.
You must choose the resources that have the right skills as well as the appropriate level of experience. Why is this important? Well, because a lesser skilled resource may misunderstand the requirements. Or they may be inexperienced in developing something exactly as expected. It may even happen that the resource is doing something correctly, but they are too slow. These reasons can cause the project to be delayed or a rework might be required on some of the activities. This, in turn, will cause project cost overruns.
If your planning is perfect, and the documentation is thorough, but your resources are not skilled enough, you will face issues. We know that managing issues will always incur costs. Therefore, you should acquire only the resources that you think have the right skills to work on your project. Based on IBM’s training report, every dollar spent on corporate training programs gives $30 in return. So, corporate companies value training their employees to increase project delivery competence.

At Master of Project Academy, we can help your employees get the right skills to manage successful projects. The key to profitable organizations is well-trained and competent employees. Let us train your employees and have them learn from our experienced instructors on how to apply the best project management practices. Your organization and your employees can choose from several certification training courses such as CAPM (Certified Associate in Project Management), PMP (Project Management Professional), and Core PM courses.
- PM Core™ – Project Management Training for Business
- PMP® Certification Training – 35 Contact Hours Online PMP Training
- PMP® Online Class Virtual Training – 4 Days – 35 Contact Hours
- CAPM® Certification Training – 23 Contact Hours Online CAPM Training
- CAPM® Online Class Virtual Training – 3 Days – 23 Contact Hours
3- Effective Risk Management
Risk management plays a very important role in keeping the project under budget. If risks are not thoroughly identified or if the proper contingency reserve is not set to cover these risks, the project will need extra money to deal with the unanticipated risks. These events will cause project cost overruns.
When there is no effective risk management in place, some risks may pop up as a surprise. You will be caught off guard as you would not be prepared to deal with them. Your first reaction will be utilizing your resources to thwart the consequences of the risks. However, this sudden dealing with the risks may require you to use resources outside the project budget. You may even have not many options to choose from in order to deal with sudden risk situations. So, you will end up doing whatsoever is possible for you to manage the risks quickly, and this may cost you a lot more money.
A project manager must make an effort to consider all the possible scenarios. To do that, they should use experience, historical data, and brainstorming to identify the risks. Yes, the risks should also be found throughout the project, but early identification is far better. So, once the risks have been identified, each risk should separately be assessed for its probability, impact, and priority. Risks may also be categorized. Categorization could be based on safety, technical, financial, internal, external, resources, or other criteria, as suitable. Categorization helps the project manager to understand where the maximum level of uncertainty lies. It also helps in monitoring and reporting purposes. With every risk, the appropriate amount of reserves must be calculated and kept.
By attending any of the courses (PMP Certification Training, CAPM Certification Training, or Core PM) offered by Master of Project Academy, the project managers and other employees involved in project executions will receive a practical and in-depth understanding of how to identify, classify, analyze risks and apply proper risk management techniques specific to their projects. Our instructors will provide the participants with real-life examples and case study scenarios on how to effectively manage risks, and determine realistic contingency reserves.
4- Train Project and Non-Project (External) Stakeholders
We often ignore the fact that people can also cause project cost overruns. Usually, the project manager focuses on the project activities, project documents, and the resources necessary to complete the project. However, they should also consider the fact that untrained people involved indirectly in the project, with no fundamental project management knowledge or enough experience, may also be an obstacle to success. That is why we have launched PM Core™ – Project Management for Business People Training program to create project management awareness among non-project people.

Work done by untrained non-project resources (people who are external to the project and are not directly involved in project work) can actually make things quite complicated. They are not aware of the processes that they need to follow. Furthermore, no one is centrally controlling them, and they do not tend to work according to project plans. So, untrained resources could, for instance, cause inefficiencies in work, produce errors in deliverables, or make wrong decisions. The negative impact of untrained people could be insignificant, but it could also be disastrous for the project. Issues caused by untrained people could require product repair or rework. This would consequently lead to project cost overruns.
How to Manage Project Cost Overruns
No one wants a project cost overrun. However, if it happens, what are the ways to overcome and manage the overruns? Read on for effective ways to manage project cost overruns.
1- Make Sure the Project Cost Overruns Are in Your PM Limits
Every organization has a different level of PM authority. In some cases, there are allowed cost and schedule delay limits that a PM may use to manage the overruns. For e.g. a PM might be allowed to manage a project with up to 5% deviance in budget and 7% schedule delay.
No one should take advantage of this though. Even if there is a cost overrun limit, the PM should try to adhere to the planned budget. Adhering to the planned budget not only saves the organization money but also reduces waste. If for any reason, the cost overruns are beyond the limits, the PM should act soon. They should try to bring the overruns within acceptable limits.
In a situation when cost overruns happen, the PM should be able to handle this situation. They should look at the various ways as well as the project priorities to bring the spending under the limit. They should also consult with the key project stakeholders to find a mutual and effective solution.
The cost baseline serves as a reference for measuring and controlling cost performance. So, the PM should keep a constant eye on the cost baseline and the actual cost, in order to identify possible cost variance. The Project Manager can do it by utilizing several cost measurement tools. For instance, they can look at the cost S-curve or the cost histogram. By looking at these visual graphs, they will be able to recognize the amount of deviance in the cost. Based on these findings, they would be able to determine the best course of action necessary in that situation.
2- Assess Make-Buy Decisions
Both the options, make and buy, have their own pros and cons. The make-or-buy analysis is conducted at both the operational and strategic levels. Whether to buy or make depends on many factors. The organizations choose the option that is most suitable and cost-effective for the project.
When buying, you do not need to worry about your expertise and the management of the making process. On the other hand, the in-house making of the product gives you better control of the product. You can customize it however you like. There is no need to establish and adhere to any contractual terms or conditions. Cost is the common factor in both options. The project manager would determine both the make and buy options along with the other factors and decide what to do.
In some cases, however, buying might be more budget-friendly than making it in-house. It is because you don’t have to spend on the infrastructure and the resources needed to make the required product or component. For either of the options, the PM should analyze the project requirements, the available budget, the schedule, and other constraints. After the proper analysis, the PM can assess if there are certain work packages that can be outsourced and accomplished at a lower cost.
3- Use Contingency Reserves to Minimize Overrun Impacts
No project goes 100% as per plan and this is a universal fact. There are always many factors that trigger the need to overspend. Although there may be a need to spend more money than initially planned, overspending will cause project cost overruns and negatively impact the project’s reputation.
Hence, there should always be contingency reserves in the project for unforeseen expenditures. The reserves could be kept at the project level, work packages level, or at activities level. And since the reserves are part of the approved budget, utilizing them in certain situations wouldn’t harm the project. So, project managers should make sure that they determine the number of contingency reserves for unforeseen expenditures. This can only be done with the help of effective risk management.
You should never calculate contingency reserves based on assumptions. Rather, you should calculate it using various risk management techniques. For example, you can use the risk register to track the identified risks and calculate the Expected Monetary Value of the identified risks if they happen. The Expected Monetary Value analysis will help you determine more precisely the number of Contingency reserves you will need on the project. The project managers have full authority to use this reserve and they control it. When the need arises, they can decide how much of the reserve to use and for which activity.
Most often, the contingency reserves tend to be lower near the end of the project and higher near the beginning. With the help of graphs and charts, the PMs can track the use of the contingency reserves over time and manage it for the best outcome.
In addition to protecting project cost overruns, another use of contingency reserve is that you can use this information to communicate the project’s risk profile to stakeholders. Hence, contingency reserve is a valuable risk response strategy that protects the project against cost overruns and it should be part of every project planning.
4- Consult Your Superiors
If the project is about to face cost overruns, it is appropriate to use the allocated contingency reserve. But what if the cost overruns are more than your set limits? In this situation, you would not have a contingency reserve anymore. Therefore, you need to consult your seniors and act immediately. Your organization must have set a management reserve to overcome risks worth more than your contingency reserve. Use management reserve if approved in this situation.
Management reserve is often derived from a percentage of the overall project budget. How much management reserve will be allocated may depend on the type of project. It also depends on how much of the project cost overruns you want to manage. And often, for research and development projects, the reserve is higher and for known product development, the reserve is lower. However, the project manager can also look at other ways to determine the management reserve. For example, they can look at the performance of similar past projects and then determine an appropriate management reserve.
Summary
Managing a project with cost overruns is not unusual. Doesn’t matter what type of project, whether IT, construction, medical, or any other, cost overruns can occur in any project. Any project can have a cost overrun but large or complex projects tend to experience cost overruns more. Conditions beyond human control could impact the project cost such as extreme weather, inflation, etc. However, most of the time there are other reasons for project cost overruns. Inadequate analysis, inadequate planning or incorrect estimation, and other factors like these are mostly the causes of cost overruns.
In this post, we explained some of the common reasons for project cost overruns. We also explained the ways to prevent and manage the overruns. Among the factors associated with cost overruns, risk management is something that organizations shouldn’t overlook. Some threats even have the power to really harm businesses. High-cost deviations can cause undesirable results, such as canceling or postponing the projects, reduction of the project scope, and loss of public trust.
Planning and utilizing the project’s contingency and management reserves is one of the best ways to manage project cost overruns. Instead of allowing the project costs to exceed the budget, it is better and more acceptable to use the reserves and still stay under the budget.
By attending any of the courses (PMP Certification Training, CAPM Certification Training, or Core PM) offered by Master of Project Academy, the project managers and other employees involved in project execution will receive a practical and in-depth understanding of how to identify, classify, analyze risks, and apply proper risk management techniques specific to their projects. Our instructors will provide the participants with real-life examples and case study scenarios on how to effectively manage risks and determine realistic contingency reserves. Knowing how to manage risk properly will help you run projects on schedule, and within cost and deliver successful projects that meet customers’ expectations.
Unlock the undiscovered project delivery competence of your organization.
We’ve helped 200,000+ professionals enrolled from 100+ organizations including these reputable organizations.
We can enhance your organization’s competence too! View our corporate services and training.

