ITIL training teaches us that the ITIL service management lifecycle has several components. The ITIL problem management process is one of these components. Within ITIL, it is mainly a process of the ITIL Service Operation stage. However, it also pops up in other stages of the ITIL lifecycle.

Some problems are received by the service desk, so ITIL problem management is directly linked to incident management. As a problem may have a financial impact, the ITIL problem management process also links to financial management. Even though the ITIL Service Design stage occurs upstream in the ITIL service lifecycle, past and present problems which were addressed by ITIL problem management are considered in the ITIL Service Design stage as part of knowledge management. Finally, ITIL problem management also links to ITIL continual service improvement where problem management occurs proactively. The ITIL problem management process is important for long-term service delivery and should form part of a robust IT service. In order to do so, it’s important to understand the ITIL problem management process flow as discussed in
The ITIL problem management process is important for long-term service delivery and should form part of a robust IT service. In order to do so, it’s important to understand the ITIL problem management process flow as discussed in ITIL foundation certification training.
ITIL problem management process flow: receiving problems
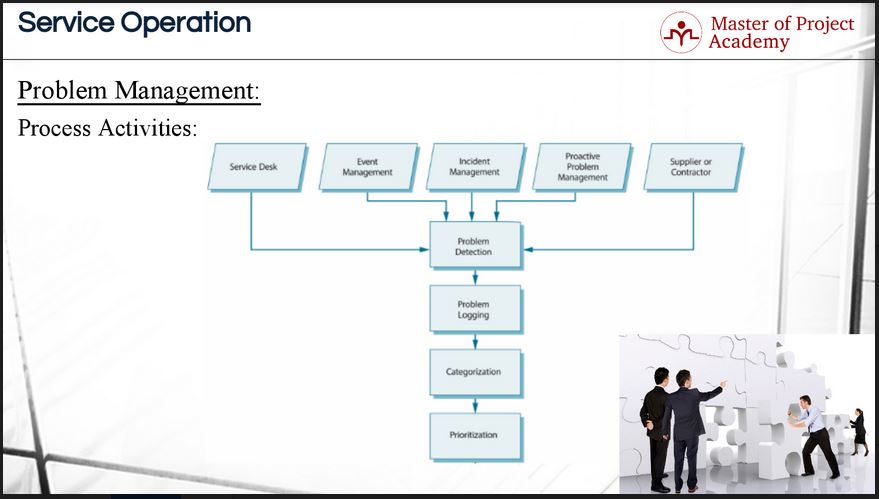
A problem is received by the ITIL problem management process through different channels. These are the service desk, event management process, incident management process, proactive problem management, and supplier or contractor. After the problem is received, the next step in the ITIL problem management process is that the problem is
After the problem is received, the next step in the ITIL problem management process is that the problem is detected and if it is really a problem, it is logged in the system. A problem record is a database in which every problem in an IT service provider is compiled. There are many ways to log a problem as part of the ITIL problem management process. It could be handled via a ticketing system for example. Important data needs to be captured such as the time and date of the occurrence, the related incident, the symptoms, previous troubleshooting steps etc. Capturing all relevant information helps the team to find the root cause of the problem which is an important part of ITIL problem management.
There can be several problems occurring in an IT Service Provider. So, as with incidents, problems are categorized as the next step. The same categories that are used in incident categorization should be used for problem categorization. A main and a secondary category could be assigned. This helps with sorting the categories regularly and with reporting on problems which help the organization to track trends.
After the problem was categorized, it is prioritized to deal with the most important problem first and less important or less impacting problems later. Prioritization is an important step in ITIL problem management. Priority is based on the impact of the problem on users, on the business and its urgency. Urgency is defined as the timeframe in which the business needs the problem resolved. The impact is defined as the extent to which the problem could cause damage to the business. Prioritizing problems helps the IT service provider to use its resources more effectively in problem-solving.
Investigation
In the next step, problems are investigated and diagnosed based on their priority respectively and details are recorded and updated in the configuration management system.High-priority problems should always be dealt with first as their impact on the business is the greatest. During diagnosis, the incident related to the problem is analyzed and any further testing that is beyond the scope of the service desk is done.
After initial investigation and diagnosis, the next step is to check to see whether there is any workaround available for the problem which can be used to avoid impacting on the users until the problem is fixed permanently. A workaround helps the service desk to restore services with a temporary solution until the real cause of the problem can be solved. Problems can take months to resolve which is why it is so important to have workarounds for problems. Workarounds are critical in ITIL problem management.
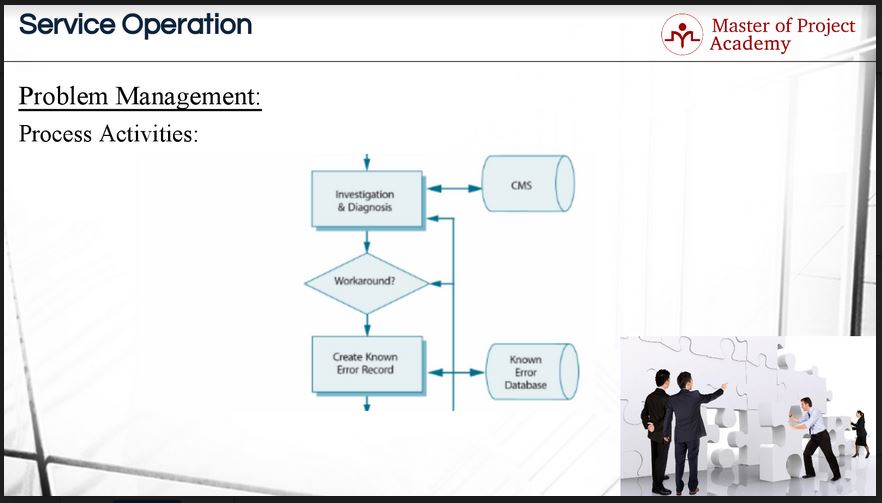
Then, the problem is recorded in the known error database with its workaround. In this way, if the same problem is reported again, the personnel of the IT service provider will see the known error record and apply the workaround to overcome the impacts of the problem. When a workaround is documented, service personnel can use the workaround to deal with the problem quickly as it occurs.
Change management
In the next step, a resolution is found for the problem to fix it permanently. Resolving a problem means that the root cause of the problem has been identified and that a troubleshooting solution has been identified. In next step, it is checked whether the solution of the problem requires a change. If change is required, change management process is triggered, a request for change is initiated to evaluated and implement the change. One example is that the solution might require a change in service levels. Let’s consider a database change that may cause the service to slow down during the changeover. Risks should be considered before implementing the solutions. And after tests and checks, if the problem has been fixed permanently, the problem record is closed. At this stage, since the permanent solution for the problem is delivered, the known error database is updated and the record is removed.
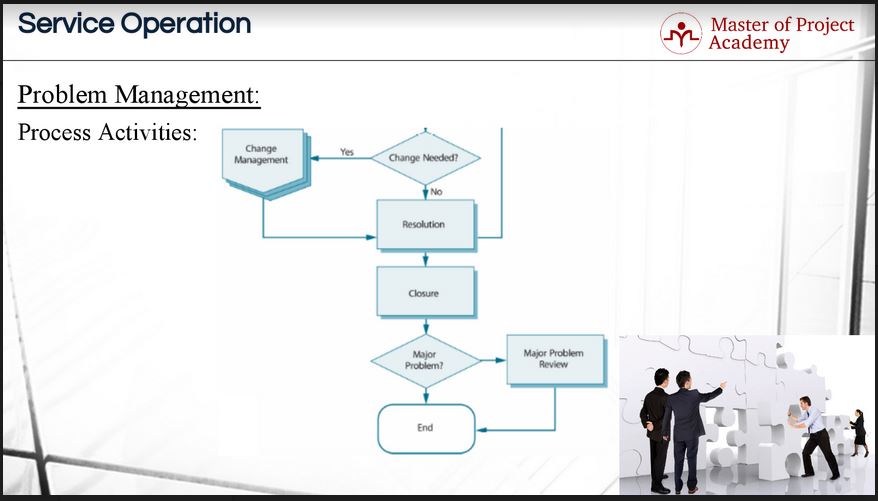
After the closure of the problem, if it is a major problem, major problem review is executed. The major problem review is a process step necessary to avoid future problem. The problem management team will look at all the problem records and identify exactly what went wrong. Lessons learned and review results about the problem are discussed and logged in the service knowledge management system for future reference. And the continual service improvement stage looks for improvement actions and communications to prevent similar problems from occurring in future again.
And these are the steps of this process. Following these steps when a problem occurs is an organized way of dealing with problems and avoiding the same problems in the future. This ITIL approach minimizes the impact of problems in the business.
Review by: Freddie Carroll
