No matter how well you plan a project, actual results will differ from what you have planned. In terms of schedule, the actual durations of tasks can take longer than planned. In order to meet the project deadline, you need to take corrective actions to get back on track and these are called schedule compression methods.
Attend our 100% Online & Self-Paced One-Hour Free PMP Training.
As explained in the PMI certification training, schedule compression helps you to get your project back on track. In this article, we are going to see schedule compression definition. There are two methods for schedule compression, so we are also going to review what is crashing in project management and fast tracking project management definition.

Schedule Compression Definition
Schedule compression techniques are applied during develop schedule process if a project is behind the schedule. The objective of schedule compression is to try to compress the schedule without changing project scope. Because, if a project scope has not changed, and if the project is behind schedule, you can meet the planned deadline only by compressing the remaining schedule of the project.
There are 2 approaches for schedule compression according to project management certification courses. Let’s go over each schedule compression approach one-by-one.
The 1st schedule compression technique: What is fast tracking in project management?
First approach is Fast Tracking. Let’s give fast tracking project management definition. In fast tracking schedule compression technique, critical path activities are performed in parallel instead of series. This is possible only the activities are not in mandatory dependency. Because, if two activities are depending on each other by nature, you cannot do these two activities in parallel. For instance, you cannot start testing of a screen before completing development. If critical path activities are depending on each other because of resource dependency or if there is a discretionary dependency, you can fast track those activities to complete remaining activities faster.
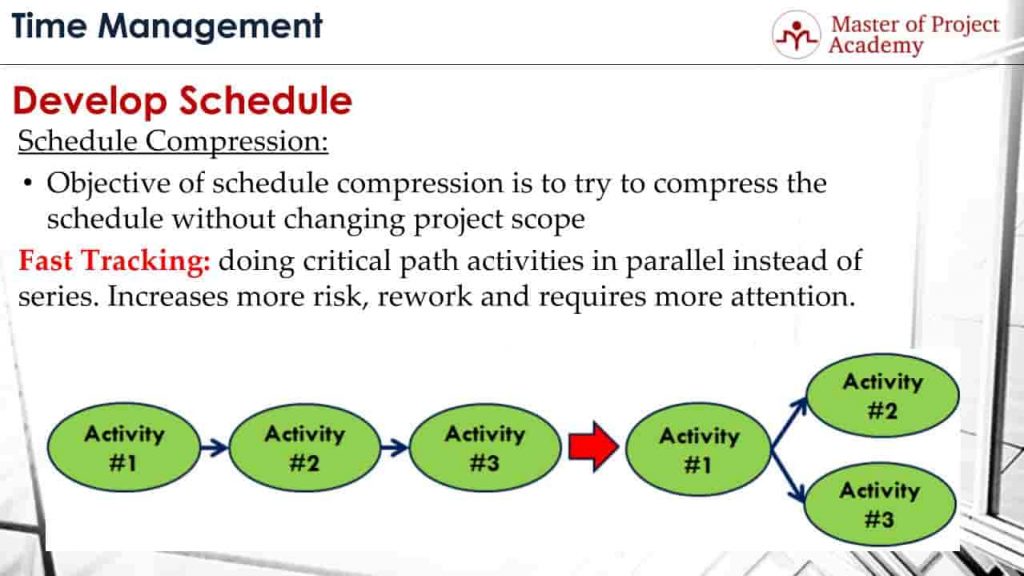
Let’s visualize fast tracking over a sample. As a fast tracking example, let’s consider that there are 3 activities that need to be completed each other: Activity #1, Activity #2 and Activity #3. If you are aiming to finish the project faster, you can perform Activity #2 and Activity #3 in parallel after completing activity #1. This is called fast tracking schedule compression approach.
The 2nd schedule compression technique: What is crashing in project management?
Second technique is crashing. In crashing schedule compression technique, there is a trade-off between cost and schedule. If the scope is the same and project is behind schedule, another option for compressing the schedule is putting extra resources on remaining activities of the project. Because if it is possible to assign more than one resource on an activity, activity duration will decrease respectively. This will help to complete the project faster. However, since these extra resources were not in the initial plan, there will be an additional cost if crashing is used for schedule compression.

5 major steps to follow if the project is behind the schedule
If a project is behind the schedule, there are 5 major steps that must be followed in sequence.
- First, check risks and re-estimate. Because, for the remaining activities, if the risks that were considered during planning are no longer valid, re-estimation of the remaining activities can result in shorter activity durations. Re-estimation will show how long will it take to complete remaining activities of the project.
- If re-estimation results in a later deadline for project completion, Fast-tracking the project must be considered. Remaining critical path activities are evaluated and possible activities that can be performed in parallel can be done to shorten the duration of the project. This is one of the advantages of fast tracking in project management over crashing because fast-tracking does not bring an extra cost to project.

- The third step is crashing the project. Extra resources are planned and extra budget is allocated to accommodate the increasing costs. Since more resources will work on remaining activities of the project, it is expected to finish the project on time.
- The fourth step is scope reduction. Reducing the scope can help to reduce the remaining activities in the project and if the customer agrees, reducing the scope can help to complete the project on time.
- The fifth step is cutting the quality. Achieving a certain level of quality means cost and time. If the customer agrees to decrease its quality expectations, cutting quality can help you to complete the project faster. Note that, 4th and 5th steps are not recommended the course of actions in a project.
Review by: Robert Phillips



One thought on “2 Techniques for Schedule Compression: Fast Tracking & Crashing”
Comments are closed.